4.8.2. Elements
[4.8. Meshes]
Table 4 Element Types
-
Type 003-008 are Junction Elements with 3-8 nodes. Each is a 0D element that joins several 1D elements. The number of elements joined is the same as the type. The nodes in a junction element are all at the same position and are attached to other 1D elements.
-
Type 100 is a 1D linear element with 2 nodes.
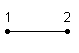
-
Type 101 is a 1D quadratic element with 3 nodes.
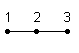
-
Type 110 is a Transition element (1D-2D) (RMA2 definition) 1 is connected to a 1D element. 3,4,5 are connected to a 2D element with 5 nodes.
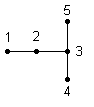
-
Type 200 is a 2D linear triangle with 3 nodes.
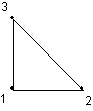
-
Type 201 is a 2D quadratic triangle with 6 nodes.

-
Type 210 is a 2D linear quadrilateral with 4 nodes.
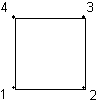
-
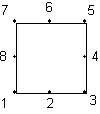
Type 211 is a 2D quadratic quadrilateral with 8 nodes.
-
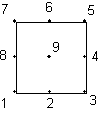
Type 212 is a 2D quadratic quadrilateral with center node with 9 nodes.
-
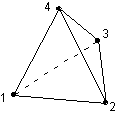
Type 300 is a 3D linear tetrahedron with 4 nodes.
-
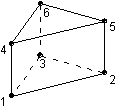
Type 310 is a 3D linear prism with 6 nodes.
-
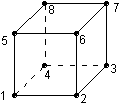
Type 320 is a 3D linear hexahedron with 8 nodes.
-
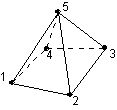
Type 330 is a 3D linear pyramid with 5 nodes.
Element Activity and Material IDs Element activity and material ids can be stored as properties under the element group. Management of property groups is described in section 4.7. The reserved names for element activity and material ids are "Activity" and "Material."
Coordinate System The options for storing the coordinate system for a mesh is discussed in section 4.13.
 1.5.6
1.5.6