4.12. Data Sets
[4. Implementation Design]
Modules | |
| 4.12.1. API Functions | |
| 4.12.2. Properties | |
Detailed Description
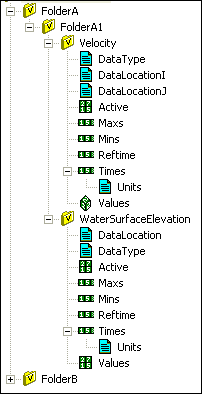
Data sets are sub groups associated with another group (a mesh, grid or geometric path group). They are stored in a special folder (group) that contains sub-folders for individual data sets. Data sets can be either scalar (a single value per geometric entity) or vector (2 or 3 values per geometric entity).Scalar data sets are stored as a two-dimensional array where the first index is the time step index and the second index is the node or cell index.
Vector data sets are stored as a three-dimensional array. The first index is for the time step, the second index is for the node or cell, and the third index is for the individual components. The first index (0 in C, 1 in FORTRAN) corresponds to the x component, the second index corresponds to the y component, and the third index corresponds to the z component. For grids the components may be in I, J, K coordinates rather than x, y, z.
The data locations for meshes are always at mesh nodes. Data locations for grids may be at centers, nodes, all faces, or only on faces in a particular direction (one value per cell). The data locations for vector data sets may be different for each component. For example, the two-dimensional hydraulic model M2D computes and reports velocities at cell faces. Velocity in the I direction is given at cell faces perpendicular to the I direction. Likewise, velocity in the J direction is given at cell faces perpendicular to the J direction.
Particular elements or cells may have values at one time-step but not have values at another. This happens frequently in hydraulic models. When flow rates are decreasing areas that are inundated can dry, leaving an area of the mesh dry that was previously wet. These situations are handled by an optional activity array. This activity array is a two-dimensional array of on/off values indicating whether a specific element or cell is active for a given time step and element or cell. Activity arrays are always done on a cell-centered basis regardless of whether the data is mesh or cell-centered. The Activity array is a two-dimensional array where the first index is the time step index and the second index is the cell or element index.
Data sets stored using XMDF include the minimum and maximum values for each time step. Although this information is not necessary for a data set, it is useful for visualization packages. The minimum and maximum values are automatically determined when data sets are written using the XMDF API.
Because data sets can take up large amounts of disk space, XMDF allows data sets to be compressed. Compression is performed using the default compression algorithm in HDF5.
 1.5.6
1.5.6